Understanding and mastering your product’s journey is the secret to building effective marketing and business strategies. The product life cycle refers to the phases a product goes through, from initial conception and growth to its eventual withdrawal from the market.
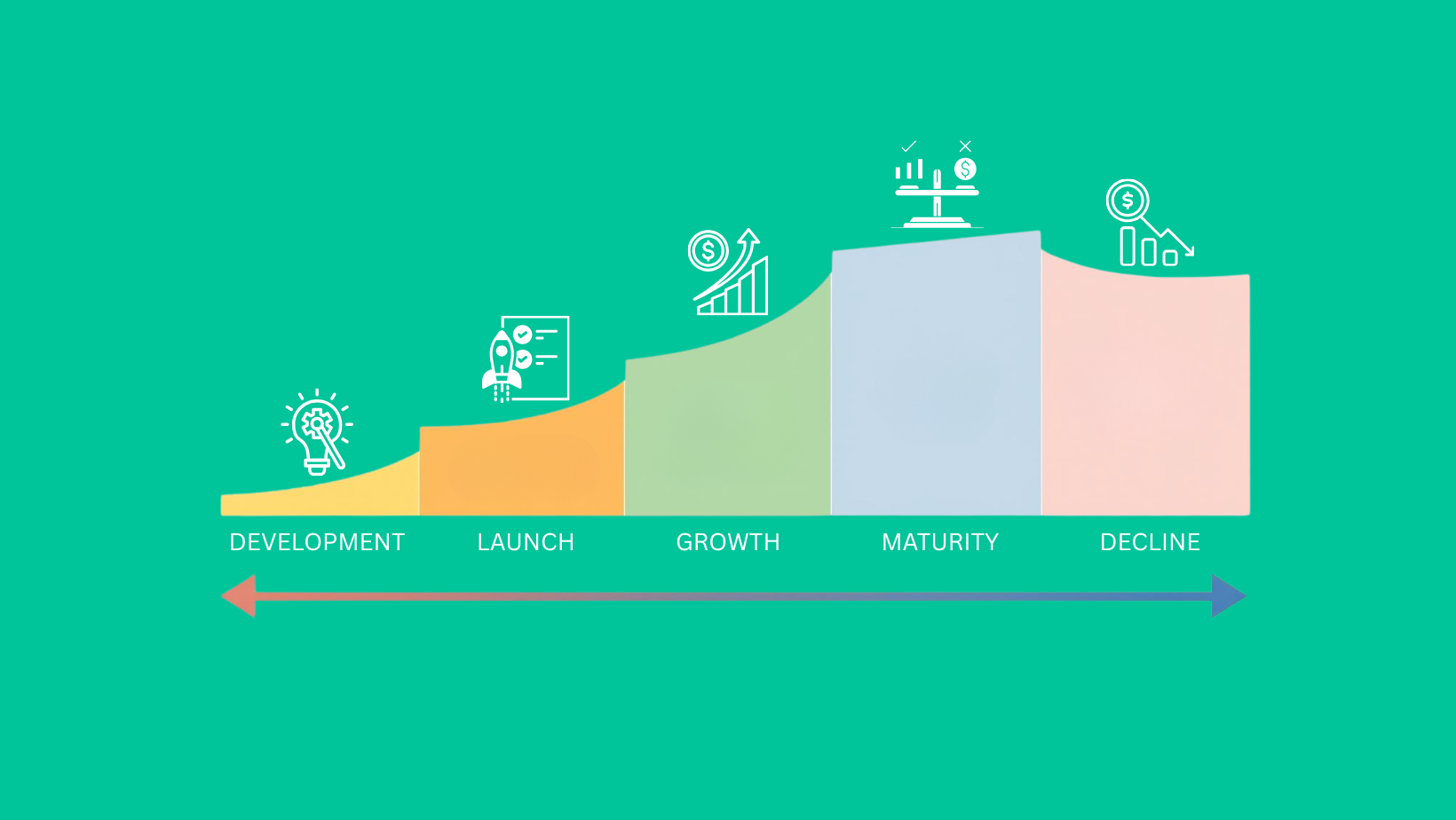
Generally, this process is organized into the 5 stages of the product life cycle: development, introduction (launch), growth, maturity, and decline. By precisely understanding how to maximize potential at each stage, companies can improve profitability and extend the product’s lifespan with consumers.
If you have invested resources without seeing the expected results, this strategic look into the product life cycle will provide the perspective needed to ensure your business’s growth.
Hakuna Matata! 🦁
Understanding the Concept
Introduced by economist Theodore Levitt in 1965, the product life cycle remains an essential concept for any business today. Mastering this journey enables a company to implement strategies tailored to each phase and remain profitable.
It is important to note that while the cycle has a clear beginning and end, each stage does not have a fixed duration. The time spent in each phase depends entirely on the product type and the market environment.
The 5 Stages of the Product Life Cycle
1. The Development Phase
This is the “conception” stage, where you design the product. Following market research and framing workshops, you refine the concept and test its viability with your target audience.
- De-risking: Most companies start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) or prototype to limit costs and identify uncertainties early. This ensures the product meets user expectations before full-scale development.
- Investment: At this stage, the product generates no revenue; it is strictly an investment phase.
- Modern Approaches: Using NoCode tools and Agile methodologies is ideal for building, testing, and launching faster and at lower cost than traditional coding.
2. The Introduction (Launch) Phase
This is when your product officially launches. The primary goal is to build awareness among your target audience.
- Marketing Responsibility: Success often depends on marketing campaigns (advertising, social media, events) to drive commercial promotion.
- Variables: Success isn’t guaranteed; it depends on the degree of innovation, the level of competition, and the clarity of your message.
3. The Growth Phase
If the launch is successful, the product enters the growth stage, marking the beginning of profitability.
- Market Adoption: Users begin adopting the product, and revenue begins to climb.
- Goal: Maintain this phase for as long as possible.
- Strategy: You must continue to conquer market share by analyzing user data and iterating on the product, adding new features, expanding to new channels, or broadening your target audience.
4. The Maturity Phase
During this stage, sales begin to stabilize. While the product remains profitable, growth begins to stagnate.
- Competition: The market may become saturated, and competition becomes fierce.
- Strategy: Marketing efforts shift toward highlighting pricing advantages and key differentiators to remind customers why your product is superior.
- Preparation: This is the time to start investing in the development of a new product to anticipate the eventual final stage.
5. The Decline Phase
Eventually, most products enter a decline. Users may lose interest or move toward more innovative alternatives.
- Triggers: Factors include high competition, product obsolescence, or a weakened brand image.
- The Choice: At this crossroads, you must decide whether to retire the product and focus on a new idea or attempt to innovate on the existing product to reverse the trend.
Why Mastering the Product Life Cycle Matters
Understanding these stages allows a business to:
- Make better business decisions.
- Develop tailored marketing strategies for each phase.
- Increase overall profitability.
- Improve customer relationships and loyalty.
- Stand out from the competition.
Factors Influencing the Product Life Cycle
The speed and success of the product life cycle are influenced by several internal and external factors:
- Innovation Diffusion: Based on Everett Rogers’ theory, a product’s adoption depends on how well it is differentiated and how closely it meets user needs.
- Technology Speed: In fast-moving tech sectors, product lifecycles are typically shorter, requiring continuous improvement to stay competitive.
- External Factors: Macroeconomic events, such as the 2019 pandemic, can drastically shift a product’s lifecycle overnight.
By taking a proactive, strategic approach at each stage, from development through decline, you can maximize your product’s profitability and long-term relevance in an ever-changing market.
BluDeskSoft supports this journey as your innovation partner, providing the technical expertise needed to adapt to the ever-evolving tech ecosystem. Our team of professional problem-solvers specializes in creating tailored software solutions and intricate database systems, meticulously crafted to deliver reliable, long-term performance across every stage of the product life cycle.
Do you have a project in mind for any of these stages? Contact us and let’s shape the future of your technology together!